What is a lithium-ion battery? Types of lithium-ion batterie
Lithium-ion Battery or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that is charged and discharged by lithium ions, it is an advanced technology that uses lithium ions as a key component. During a discharge process, lithium ions move between the anode(negative) and cathode(positive) electrodes. The lithium ions are very small to be able to move through a micro-permeable separator between the cathode and anode.
Lithium-ion batteries are utilized in a wide range of applications, including consumer devices such as smartphones and PCs, industrial robots, production equipment, and automobiles since they are capable of storing high-capacity electricity.
What are the components of lithium-ion batteries?
Four major components make up a lithium battery. The cathode is the source of lithium ions and regulates the battery’s capacity and voltage. When a battery is charged, lithium ions are stored in the anode, allowing electricity to flow through an external circuit.
Salts, solvents, and additives make up the electrolyte, which acts as a channel for lithium ions between the cathode and anode. Finally, there’s the separator, which acts as a physical barrier between the cathode and anode.
How do lithium-ion batteries store energy?
There are main components of a Lithium-ion battery
- The cathode and anode
- A separator between the two electrodes
- To fill the remaining space of the battery, there is an electrolyte
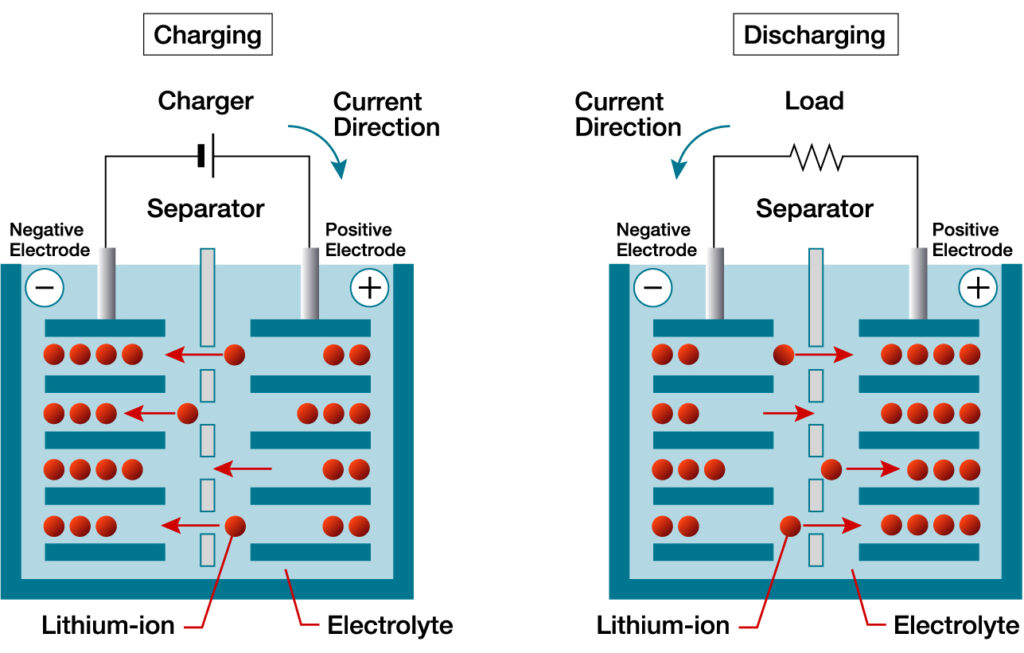
Both the anode and the cathode may store lithium ions. The electrolyte transports lithium ions between the electrodes, storing and releasing energy.
Types of Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are available in a range of shapes and sizes, and they are not all created equal. Six different lithium-ion battery types are described below, along with their compositions and common applications.
Lithium Cobalt Oxide
Lithium cobalt oxide batteries are constructed of lithium carbonate and cobalt and are also known as lithium cobaltate or lithium-ion cobalt batteries. Because of their high specific energy, these batteries are employed in cell phones, laptop computers, and electronic cameras. During discharge, lithium ions travel from the anode to the cathode, with the flow reversing when the battery is charged. They are equipped with a cobalt oxide cathode and a graphite carbon anode.
It has some drawbacks like poor power and short battery life. Also, these types of batteries are not safe compared to other lithium-ion batteries. Despite this, these are very popular for smartphones and other compact electronic gadgets..
Lithium Manganese Oxide
Lithium manganate batteries, lithium-ion manganese batteries, li-manganese batteries, and manganese spinel batteries, lithium manganese oxide batteries are a type of lithium manganese oxide batteries. The first publication of this sort of battery technology came in the 1980s, with the initial publication in the Materials Research Bulletin in 1983. Moli Energy was the first company to commercialise lithium-ion batteries with a lithium manganese oxide cathode in 1996.
Lithium manganese oxide batteries are distinguished from others by their high-temperature stability, and they are also safer than other lithium-ion battery kinds. As a result, they’re commonly found in medical devices and equipment, but they can also be used in power tools, electric motorbikes, and other uses. Laptop computers and electric vehicles can both benefit from lithium manganese oxide batteries.
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP)
In lithium iron phosphate batteries, often known as li-phosphate batteries, phosphate is used as a cathode. Their low resistance properties increase the thermal stability and safety of the product.
LFP is a famous, low-cost cathode material for lithium-ion cells that is noted for its high load currents and long life duration, making it ideal for specialty battery applications needing high load currents and endurance.
- Awesome and fast charge and discharge rate capability
- Low-temperature performance that is really incomparable
- Stable resistance
- In high-temperature conditions, stable voltage drop during life cycle assessment
According to these awesome features, these batteries are commonly found in electric motorcycles and other applications that require a long lifecycle and high levels of safety. Electric vehicles frequently use these batteries as well.
Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC)
Like other lithium-ion battery types, NMC batteries can have a high specific energy density or specific power. They cannot, however, have both characteristics. The most popular applications for this battery are power tools and car powertrains.
The nickel, manganese, and cobalt (NMC) formula is typically 33% nickel, 33% manganese, and 33% cobalt. Because of the lower material cost associated with a lower cobalt percentage, this blend, also known as 1-1-1, is a common choice for mass-produced cells in applications requiring frequent cycling (automotive, electronics)
Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide
A lithium nickel cobalt aluminum oxide, or NCA, the battery is comparable to the NMC in that it has high specific energy, good specific power, and a long life cycle, making it a viable option for electric vehicles. Safety and expense, as well as recent supply chain difficulties, are the key drawbacks.
Advantages of Li-ion batteries:
Lithium-ion batteries provide a number of advantages over lead-acid and other lithium batteries, including increased discharge and charge efficiency, a longer life period, and the ability to deep cycle while preserving power. LiFePO4 batteries have a greater initial cost, but a lower total cost during the product’s lifetime. They are a worthwhile investment and a sensible long-term option because they require no maintenance and have a very long lifespan.
Below are some awesome benefits of lithium-ion batteries
Eco-friendly:
In comparison to other types of batteries, such as lead-acid and nickel-cadmium (NiCd), lithium-ion batteries contain very low quantities of harmful heavy metals. Cadmium, lead, and mercury have long been used in batteries, but extended exposure to these metals, as well as improper disposal, can be dangerous to humans, animals, and plants. Despite the fact that Li-ion batteries are safer than many other types of batteries, appropriate recycling is still required, therefore never throw your used batteries away with your ordinary trash.
Lightweight and compact:
Lithium and carbon electrodes, which are typically used in lithium-ion batteries, are lightweight on their own, resulting in batteries that are much smaller and lighter than their older counterparts, such as lead-acid batteries. A typical 51Ah (= ampere-hour) lithium-ion battery weighs around the same as a 24Ah lead-acid battery (roughly 6-7kg), but has more than twice the capacity.
High energy density:
Lithium is a highly reactive element that can release and store enormous amounts of energy, allowing li-ion batteries to fit a big amount of energy into a compact space. As a result, lithium-ion batteries can go far longer between charges than other rechargeable batteries while still performing at a high level.
Very low maintenance:
Older rechargeable batteries, such as nickel-cadmium or nickel-metal hydride batteries, had a “memory effect,” or “lazy battery effect,” which meant that if they were repeatedly partially discharged before being recharged, the battery would eventually only deliver the amount of energy used during the partial discharges before the voltage dropped. To avoid this, NiCd and NiMH batteries would need to be fully discharged and recharged on a regular basis.
Lithium-ion batteries don’t have a memory effect, so they always give up their last bit of power. You can recharge them whether you’ve used 100% or 25% of their capacity, and there’s no need to worry about maintenance!
Low Self-discharge rate
Lithium-ion batteries have a low self-discharge rate as well. Self-discharge is a natural, irreversible phenomenon in which chemical reactions inside batteries degrade the capacity of the battery even while it is not in use. Lithium-ion batteries’ self-discharge rate peaks at roughly 5% within the first 24 hours after charging, then gradually decreases to 1-2 percent every month. Nickel-based rechargeable batteries, on the other hand, lose 10-15% of their capacity with each charge and another 10-15% per month.
The disadvantage of Li-ion batteries:
As with any technology, there are some drawbacks that must be weighed against the benefits.
Although Lithium-ion battery technology has drawbacks, this does not rule out the possibility of overcoming or at the very least mitigating these drawbacks and achieving exceptional performance.
Below are some drawbacks of lithium-ion batteries:
Protection required:
Lithium-ion batteries and cells have a shorter lifespan than other rechargeable technologies. They must be safeguarded against being overcharged and discharged too far. In addition, the current must be kept below safe limits. As a result, one downside of lithium-ion batteries is that they require protection circuitry to guarantee that they remain within their acceptable operating limits.
Aging
One of the most critical challenges of lithium-ion batteries for consumer gadgets is their age. This is dependent not only on the time or calendar but also on the amount of charge-discharge cycles that the battery has gone through. Typically, batteries can only tolerate 500 to 1000 charge-discharge cycles before their capacity degrades. This number is rising as li-ion technology advances, but batteries will eventually need to be replaced, which might be a problem if they are integrated into equipment.
Whether or not they are in use, lithium-ion batteries age. Regardless of usage, there is a time component to the capacity loss. When storing a normal consumer lithium cobalt oxide, LCO battery, or cell, it should be partially charged (about 40% to 50%) and kept in a cold storage place. The life of the product will be extended if it is stored in these conditions.
Cost
The expense of lithium-ion batteries is a major drawback. They are typically 40 percent more expensive than nickel-cadmium cells. This is a large concern when investigating their use in mass-produced consumer goods when any additional expenses are a major factor.
Technology
Due to the fact that lithium-ion batteries have been around for a long time, some believe them to be immature technology because they are still in the early stages of development. This can be a disadvantage due to the fact that technology is always changing. However, because new lithium-ion technologies are always being developed, it can be an advantage in the sense that better options are becoming available.








You ought to take part in a contest for one of the best websites on the net. I am going to recommend this website!
Everything is very open with a clear description of the issues. It was really informative. Your website is useful. Thanks for sharing!